Temporary and nomadic coverage
Sometimes, you just need a connection for a short period of time, or while being on the move. A fixed internet connection does not give you this flexibility. A public mobile internet connection does not always provide the required quality of service, or there is simply no coverage at all! That is where temporary and nomadic wireless coverage comes into play.
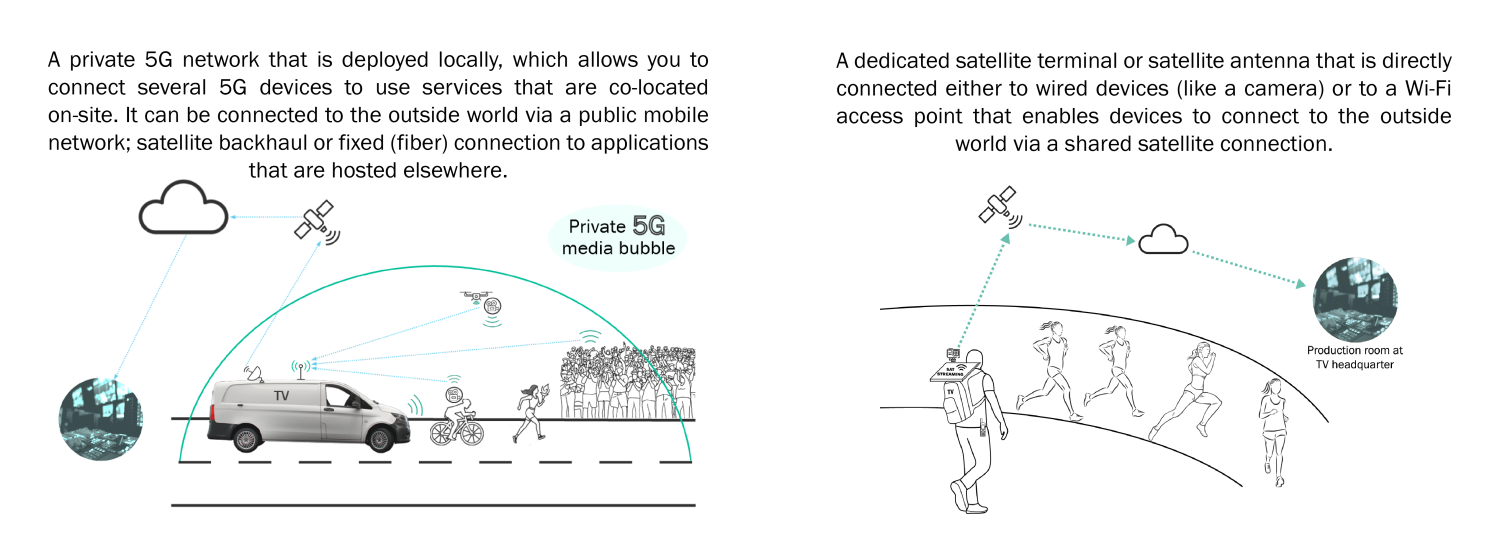
Temporary coverage provides wireless connectivity that is only used for a short period of time, like days or weeks. A network is set up to support the connection of several devices during the event or project. Nomadic coverage enables mobile wireless connectivity that can be easily relocated from site to site or remain operational while moving slowly.
Some examples that require nomadic or temporary coverage are media production during sport events, tactical communications in crisis situations, and connectivity of wireless equipment during a music festival.
Let’s take an example to compare both technologies: During a sports event, several professional cameras and smartphones capture live video feeds, which are transmitted to a central production site. Camera operators coordinate in real-time via group communication using headsets.
Different satellite constellations
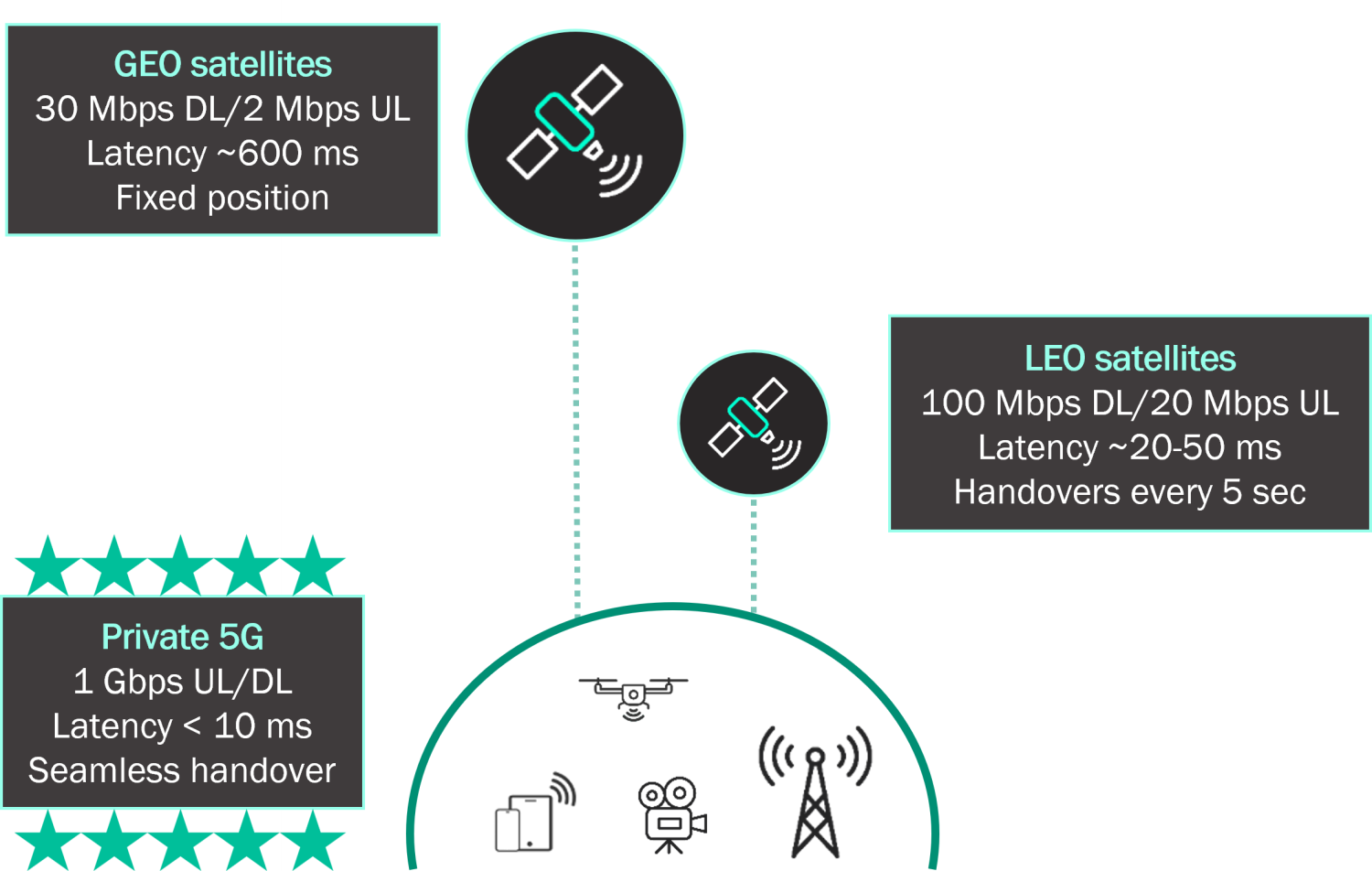
There are different types of satellite constellations: Geostationary (GEO) or Medium or Low Orbit (MEO/LEO). Each has distinct characteristics and is therefore suited to different use cases.
For low-bandwidth needs, GEO satellites are the best option. They have a fixed position relative to a point on Earth and provide coverage without interruptions caused by satellite handovers. Throughput is on average around 30 Mbps in downlink and 2 Mbps in uplink. The roundtrip latency is about 600 milliseconds. Video production use cases cannot be supported on this type of satellite, but low-bandwidth use cases that are tolerant to a higher latency could be served.
More and more MEO and LEO satellite constellations have become available for the large public, with Starlink for example, or the Eutelsat OneWeb constellation. The satellites in these constellations operate in orbits closer to Earth, which means that regular handovers need to take place between satellites to provide coverage of a specific location. The throughput that can be achieved by LEO constellations is around 100 Mbps for downlink traffic and 20 Mbps in uplink. The latency varies from 20 to 50 milliseconds. In some constellations, handovers occur every 5 seconds, compromising the stability of the connection.
Satellites connectivity is often used in rural areas. It can also be used in urban areas but requires a clear line of sight to the sky.
Benefits of private 5G
Compared to a direct satellite connection, a private 5G network offers several key advantages.
Your own private 5G network provides predictable, customizable, and controlled coverage. Exactly where you need it with the capacity that is required for your use cases. A 5G network delivers Quality of Service (QoS). If multiple services such as video and voice are used on the private network, each application gets the required bandwidth. Unlike 5G, Wi-Fi or satellite networks do not allow you to easily differentiate the quality of services for your applications.
With a private 5G network, you get coverage both outdoors and indoors. A satellite antenna requires a direct line of sight, for which indoor coverage is impossible. Furthermore, within a private 5G network, users can move seamlessly without any interruption of traffic, even if multiple antennas are deployed. This makes it possible to cover more challenging terrains and combine both indoor and outdoor areas.
A private 5G network supports commercial 5G devices. No specialized, expensive terminals such as satellite terminals are required. And you benefit from the high security that 5G provides throughout the entire network.
Where GEO and even LEO satellite throughput is limited to 100 Mbps, private 5G can locally provide high throughput up to 1Gbps. The 5G network can be configured to support more uplink capacity, making it ideal for bandwidth-heavy applications like media production, where satellite connections are even more limited in bandwidth.
Some applications such as real-time communications are very sensitive to latency or the variation of latency, also known as jitter. Private networks offer much lower latency (<10ms) compared to GEO satellite constellations, and less latency variation (jitter) compared to LEO constellations, where regular handovers and routing inside the constellation to reach terrestrial gateways cause higher jitter.
Satellite backhauling
To connect your private 5G network to external applications, different backhaul scenarios are possible. Satellite backhaul is one of them and of course suffers from the same drawbacks as illustrated above. Nevertheless, this does not have the same impact on your applications as direct satellite connectivity.
With a private 5G network, you benefit from edge computing where applications are deployed locally within the private 5G network, for example for group communication. Not only can QoS be configured in this situation, but also the required backhaul capacity is reduced.
Not all users in the 5G network need to have a line of sight with a satellite, only the satellite gateway for backhaul. Part of the users can be indoors, in more covered areas or dense streets. No specific satellite gateway integration is needed. Your private 5G network is compatible with any satellite network.
Conclusion
Direct satellite connectivity can be an interesting technology for nomadic or temporary use cases. Nevertheless, it cannot match the reliability, throughput and quality offered by a private 5G network.
The Obvios solution, Dome in a Box, delivers a private 5G network specifically designed for nomadic or temporary deployments. Housed in an ultra-compact, ruggedized suitcase weighing less than 10 kg, it is built to operate even in challenging environments. Your network can be up and running within 5 minutes, supporting standard off-the-shelf 5G devices for immediate connectivity.


